This semester, I teach the master's course
Selected Tools of Modern Theoretical Physics 2B.
Please check the courses' websites for more information. Most important, you should not forget to indicate your preferences for each problem sheet. How this work in general is explained below. In the previous semesters, I prepared and gave the following courses at the University of Wrocław:
- An Introduction to String Theory (WS 22/23),
- Classical Field Theory (tutorial WS 23/24, WS 25/26),
- Computational Methods I (WS 24/25, WS 25/26),
- Gauge/Gravity Duality (WS 24/25),
- Lie Algebras and Lie Groups (SS 22, WS 23/24),
- Quantum Field Theory (SS 22, SS 23, SS 24), and
- Selected Tools of Modern Theoretical Physics 2B (SS 25)
For completeness, as a PhD student, I also gave tutorial for
- Theoretical Mechanics, and
- String Theory I,
both taught by Dieter Lüst at the LMU Munich.
Courses
Here is an overview about my courses. For more details, please click on the course's name. Listed are the most recent completed semesters. If you are interested in any other installments, please follow the links above.
An Introduction to String Theory
 One of the greatest puzzles in theoretical physics is to find a consistent quantum theory of gravity, the only one of the four fundamental forces we do not know how to quantise yet. Although decades of intensive work, we have no conclusive answer to this problem. Currently one of the main contender in race towards quantum gravity is String Theory. It is based on a simple but far reaching idea, to substitute point-like particles with extended objects, strings and membranes. In this course, we will explore the implications of this idea. More precisely, we study the bosonic string and see that it not onl describes gravity but also gauge theories on D-branes. Gauge theories are required to describe the remainig three fundamental forces. This renders string theory to a theory of everything. The course is tailored towards master and PhD students who are familiar with
One of the greatest puzzles in theoretical physics is to find a consistent quantum theory of gravity, the only one of the four fundamental forces we do not know how to quantise yet. Although decades of intensive work, we have no conclusive answer to this problem. Currently one of the main contender in race towards quantum gravity is String Theory. It is based on a simple but far reaching idea, to substitute point-like particles with extended objects, strings and membranes. In this course, we will explore the implications of this idea. More precisely, we study the bosonic string and see that it not onl describes gravity but also gauge theories on D-branes. Gauge theories are required to describe the remainig three fundamental forces. This renders string theory to a theory of everything. The course is tailored towards master and PhD students who are familiar with
- electrodynamics
- special relativity
- quantum field theory.
Basic knowledge of general relativity is an advantage, but you also should be find if you did not have attended the GR course yet. There are many good books on the subject, four that I like are
- Barton Zwiebach: A First Course in String
- Blumenhagen, Lüst, Theisen: Basic Concepts of String Theory
- Polchinski: String Theory, Volume 1
- Johnson: D-Branes
Moreover, David Tong has some excellent lecture notes. We will have 2.5 hours of lectures and 2.5 hours of tutorial each week. Exercises will be posted here a week before the tutorial they are discussed in. Please keep in mind that active participation in the tutorials is important to pass the course. M.Sc. Luca Scala will be the assistant for the tutorials. Please fell free to contact him or me if you have any questions.
There are many other interesting approaches to Quantum Gravity and string theory is by far not the only one. There is another course this semester, Introduction to Quantum Gravity, which I highly recommend.
Important: Students will be assigned to exercise problems by the system described below, before the tutorial. Please familiarise yourself with this system and do not forget to indicate your preferences.
Additional material for the individual lectures, including the exercises which we discuss in the tutorials, will appear here in due time.
- Why, what and how - from the relativistic particle to the Nambu-Goto actionLecture06.10.2022 06:15, notes
Please note that there are no exercise assignments for the first tutorial. However, we will use a few mintues to explain how exercise problems are assigned. To prepare, it would be great if you could already follow the instructions outlined in the pdf you find under the exercise link above. For the remainder of the tutorial, we continue with the lecture. This gives us time to motivate why we need string theory, to look at the relativistic point particle and to show how it can be generalised to the string.
Note: There were some questions today in the lecture about the history of String Theory. A nice account of this topic is given by the short article arXiv:1201.0981 of John Schwarz, one of the founders of the field.
- Classical string and the Polyakov actionLecture13.10.2022 06:15, notes
- Symmetries of the classical string, especially, Weyl invarianceLecture20.10.2022 06:15, notes
- Mode expansion and open/closed string boundary conditionsLecture27.10.2022 06:15, notes
- Old covariant quantisation, Virasoro algebra and physical statesLecture03.11.2022 07:15, notes
- Physical spectrum, massless states, no-ghosts theorem, critical dimensionLecture17.11.2022 07:15, notes
- Light-cone quantisation (tutorial) and modern covaraint quantisation in the BRST formalism with bc-ghost system (lecture)Lecture24.11.2022 07:15, notes
- Conformal field theory (CFT) and operator product expansion (OPE) in a nutshellLecture01.12.2022 07:15, notes
On CFT, one could and should give a full semester course. We cannot do this here, but I try to give you a self-contained introduction. CFT is crucial to discuss interactions between strings. Therefore, we have to gain a basic understanding of it.
- Vertex operators and a first glance at string perturbation theoryLecture08.12.2022 07:15, notes
Reading: [BLT] section 6.1 and 6.2
String perturabation theory is very beautiful. It crucially depends on the moduli space of Riemann surfaces. Unfortunately, we do not have enough to look at this topic in more detail. For those of you how are interested, section 6.2 of the book by Blumenhagen, Lüst and Theisen is a very good starting point. To make you a bit more curious, here is a picutre of a tree-point vertex in the complex plane.
Much more details how it arises can be found in section 4.2 of my PhD thesis [H42].
- Low energy effective actions and compactificationsLecture15.12.2022 07:15, notes
- Closed strings on circles and T-dualtiyLecture04.01.2023 23:00, notes
- D-branes and gauge theoriesLecture26.01.2023 07:15
Classical Field Theory
This is the tutorial for the course "Classical Field Theory" thaught by prof. Frydryszak for the Master in Theoretical Physics at the University of Wrocław. Exercises will be posted here a week before the tutorial they are discussed in. Please keep in mind that active participation in the tutorials is important to pass the course. M.Sc. Achilles Gitsis will be the assistant for the tutorials. Please fell free to contact him or me if you have any questions. For information about credits points, please refer to the syllabus (in Polish) or contact prof. Frydryszak.
Important: Students will be assigned to exercise problems by the system described here at the Friday, 9:00 pm, before the tutorial. Please indicate your preferences by then.
- IntroductionLecture04.10.2023 12:00Tutorial04.10.2023 15:15, exercise
- Sine-Gordon equationLecture11.10.2023 12:00Tutorial10.10.2023 15:15, exercise
- Linear chain: Fourier transformation and HamiltonianLecture18.10.2023 12:00Tutorial18.10.2023 15:15, exercise
- Linear chain: Initial value problem and Poisson bracketsLecture25.10.2023 12:00Tutorial25.10.2023 15:15, exercise
- Minkowski space and the light coneLecture08.11.2023 13:00Tutorial08.11.2023 15:15, exercise
- Schwarz and triangle inequalitiesLecture22.11.2023 13:00Tutorial22.11.2023 15:15, exercise
- Four-velocity and four-accelerationLecture29.11.2023 13:00Tutorial29.11.2023 15:15, exercise
- Reference frames and relativistic motionLecture06.12.2023 13:00Tutorial06.12.2023 15:15, exercise
- Pseudo-Euclidean spaceLecture13.12.2023 13:00Tutorial13.12.2023 15:15, exercise
- Unitary representation of the Poincare groupLecture20.12.2023 13:00Tutorial20.12.2023 15:15, exercise
- Pauli-Lubański vector and the relativistic particle actionLecture03.01.2024 13:00Tutorial03.01.2024 15:15, exercise
- ElectrodynamicsLecture10.01.2024 13:00Tutorial10.01.2024 15:15, exercise
- Equations of motionLecture17.01.2024 13:00Tutorial17.01.2024 15:15, exercise
- Lagrangian of real scalar fieldLecture24.01.2024 13:00
- RevisionLecture26.01.2024 13:00, revision
Achilles prepared notes that summarize the most important insights of this semester. Perhaps they are useful in preparing for the exam.
Computational Methods I
 This is the mandatory Computational Methods I course of the Master in Theoretical Physics at the University of Wrocław. It is tailored towards master and PhD students who are familiar with
This is the mandatory Computational Methods I course of the Master in Theoretical Physics at the University of Wrocław. It is tailored towards master and PhD students who are familiar with
- computers and their operating systems (Linux is preferred, but Windows or MacOS will work, too)
- at least one programming language, ideally Python which we will use in the course
- classical and quantum mechanics.
There are many good books on the subject, four that I like are
- Landau , Páez, Bordeianu: Computational Physics: Problem Solving with Python
- Scherer: Computational Physics - Simulation of Classical and Quantum Systems
- Matthes: Python Crash Course - A Hands-On, Project-Based Introduction to Programming
- Johansson: Numerical Python
There will be 2 hours of lectures and 2 hours of labs each week. Exercises will be posted here a week before the lab they are discussed in. Please keep in mind that active participation in the labs and especially submitting the solution to the posed problems is important to pass the course. M.Sc. Biplab Mahato will be the assistant for this course. Please fell free to contact him () or me if you have any questions. For information about credits points, please refer to the syllabus or contact me directly.
Location: There has been a change of the lecture room. We are now in the computer lab 120 for both, the lectures and the labs.
Recordings/hybrid participation: The lectures will be streamed on YouTube with the link for each of them given below. This should help if you are not able to physically attend.
Exam: As discussed during the first lecture, we will have individual projects for the exam. If you have any project idea, we are very happy to hear about it and then decide together how to best implement it. Here are a couple of ideas which might help you
- Molecular Dynamics Simulations: Simulate the behavior of a gas or liquid using molecular dynamics. For example implement the Lennard-Jones potential and study properties like diffusion, temperature, or phase transitions.
- Quantum Mechanics Simulations: Solve the Schrödinger equation for a coherent state in the stadium billiard and compare its time evolution with the classical trajectory. Plot some of the eigenfunctions and discuss their properties.
- Monte Carlo Methods: Implement a Monte Carlo simulation of the 2-dimensional Ising model or percolation. Explore random sampling techniques, convergence properties and/or phase transitions.
- Astrophysical Simulations: which is either
- N-body simulations or
- solve the TOV equation
- Electromagnetic Wave Propagation: Model the propagation of electromagnetic waves in various media. Implement the Finite-Difference Time-Domain (FDTD) method to study wave behavior, reflection, and refraction.
- Chaos and Dynamical Systems: Explore chaotic systems, such as the logistic map or Lorenz attractor. Focus: Analyze stability, bifurcations, and strange attractors (other than the Lorenz attractor) using numerical methods.
- Quantum Computing Simulations: Simulate simple quantum algorithms (e.g. Grover's, and Shor's algorithm or quantum teleportation). Implement quantum gates and circuits using Python with libraries such as Qiskit.
Once you have chosen a project and it is approved by us, you will prepare your Python code, a small documentation and some of the most important results and submit them to us by February the 3rd 2025 here on the website in the project section below. It is only possible to submit a single file. If you have multiple files in your project, please combine them to a ZIP-archive. After this, you will have a 15-minute presentation of your results during the exam session (dates and times are also given below) followed by 5 minutes of discussion. Projects will be presented on
- 12.02.2025 in room 426 and on
- 13.02.2025 in room 124.
Please find a list of all the projects and the respective dates and times below. The presentation part is public, therefore you are encourage to join at least some of the presentations of your peers.
For the last five tutorials, there will be no assignments. Instead you have the chance to discuss problems in the yet open assignment which you have to submit until January the 31st 2024 and challenges you encounter in your project.
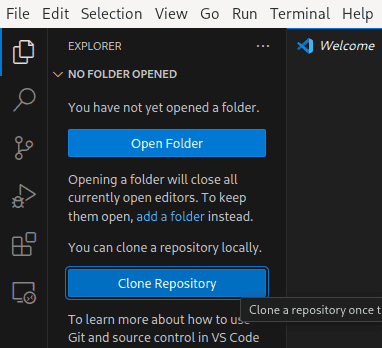
Development environment: In this course we will use the programming language Python with a notebook interface, called Jupyter notebooks. To get all this running, and avoid possible problems with incompatible versions of Python packages, we will use a standardized development environment. To set it up, please first install Visual Studio Code. On Linux, you will most likely have it already in your package manager. Alternatively, you can also download it here. Next, you need to clone the git repository for this course. To this end, open VS Code and click on the two documents (Explorer, Ctrl+Shift+E) to find something which looks like this
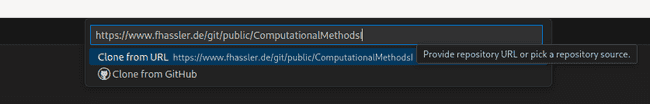
Now, click on "Clone Repository" and enter the URL of our git repository
https://www.fhassler.de/git/public/ComputationalMethodsI
like this
Finally you have to install all packages for the virtual environment, we use to run our Python code and notebooks. In the main menu, click on Terminal and then Run Build Task... (Ctrl+Shift+B). After this you should see some activity in the terminal on the bottom of the screen. If there are no errors, you have successfully installed the virtual environment. Now you are ready to add your own notebooks or run some of the already provided.
Additional material for the individual lectures, including the exercises which we discuss in the labs, is given below:
- Numerical differentiation and integrationTutorial18.10.2024 09:15, exercise
I have updated the virtual environment to include the libraries scipy and sympy. You can just pull the most recent version from the git and run the build task again (like described above) to be able to use these libraries.
- Classical dynamics with regular and chaotic behaviorLecture08.11.2024 07:30, notesTutorial08.11.2024 10:15, exercise
You might be interested to see a real, physical double pendulum after this lecture. Moreover you can play with the corresponding Poincare-map.
- Langevin and Brownian dynamicsLecture20.12.2024 07:30, notes
There are some nice examples of Langevin dynamics simulations on this website for the harmonic oscillator and for the double well potential, we already encounter in the computation of tunneling rates.
- Monte-Carlo simulationsLecture10.01.2025 07:00, notes
- Partial differential equationsLecture24.01.2025 07:30, notes
- Neural networks
The attached python implements the CNN for the digit recognition. It is a slight modification of the one given it this repository. You can add a test sample in the file test_image.png. Before runnig it, you have to install tensorflow and matplotlib. The repo for the course contains the respective virtual environment. Note that tensorflow will not work with the most recent (3.13) version of python. You have to use 3.12, which can be down with pyenv.
Gauge/Gravity Duality
 In this course, we will explore the holographic principle, stating that a volume of space can be equivalently described by its lower-dimensional boundary. One might think of a hologram which captures a three-dimensional object on a two-dimensional surface. A particular well studied realization of this idea is the AdS/CFT correspondence which conjectures the equivalence between quantum gravity in Anti-de Sitter (AdS) space and a conformal field theory (CFT) on its boundary. This conjecture is very hard to prove because when one of the two theories is weakly coupled, allowing to use perturbation theory to study it, the other one is strongly coupled - making it very hard to analyse. Despite still being a conjecture, this idea had a huge impact on high-energy physics with an extremely broad range of applications. Latter range from new insights into strongly coupled quantum field theory, required for example to study extreme states of matter like quark-gluon-plasmas or superconductors, to the analysis of black-hole evaporation, that ultimately requires a handle on quantum gravity. We take this as a motivation to study this duality and its main actors in this course in detail. The lectures are tailored towards master and PhD students who are at least familiar with
In this course, we will explore the holographic principle, stating that a volume of space can be equivalently described by its lower-dimensional boundary. One might think of a hologram which captures a three-dimensional object on a two-dimensional surface. A particular well studied realization of this idea is the AdS/CFT correspondence which conjectures the equivalence between quantum gravity in Anti-de Sitter (AdS) space and a conformal field theory (CFT) on its boundary. This conjecture is very hard to prove because when one of the two theories is weakly coupled, allowing to use perturbation theory to study it, the other one is strongly coupled - making it very hard to analyse. Despite still being a conjecture, this idea had a huge impact on high-energy physics with an extremely broad range of applications. Latter range from new insights into strongly coupled quantum field theory, required for example to study extreme states of matter like quark-gluon-plasmas or superconductors, to the analysis of black-hole evaporation, that ultimately requires a handle on quantum gravity. We take this as a motivation to study this duality and its main actors in this course in detail. The lectures are tailored towards master and PhD students who are at least familiar with
- electrodynamics
- special relativity
- quantum mechanics.
Basic knowledge of general relativity and quantum field theory is definitely an advantage, but we review their most salient aspects in case you have not yet attended a specialized course on them yet. We will mostly follow the book
- Martin Ammon, Johanna Erdmenger: Gauge/Gravity Duality,
but you might also want to have a look at
- Lewis Ryder: Introduction to General Relativity
- Michael Peskin, Daniel Schroeder: Quantum Field Theory
- Barton Zwiebach: String Theory
for more details on the main actors of the gauge gravity duality.
We will have 2 hours of lectures and 2 hours of tutorial each week. Exercises will be posted here a week before the tutorial they are discussed in. Please keep in mind that active participation in the tutorials is important to pass the course. M.Sc. Luca Scala will be the assistant for the tutorials. Please fell free to contact him or me if you have any questions.
Important: Students will be assigned to exercise problems by the system described here, before the tutorial. Please familiarise yourself with this system and do not forget to indicate your preferences.
Exam: We decided to have an oral exam (not longer than 45 minutes) for this course in the afternoon of Tuesday, the 11th of February 2025. The exact time will be individually assigned. To help you prepare, here is a preliminary list of relevant topics:
- Anti-de Sitter space
- isometries, and the corresponding isometry group
- construction as hypersurface embeed into
- bounday and its properties
- different coordinate systems
- Large N limit of SU(N) (super) Yang-Mills theory
- planar diagrams
- relation of the partition function to the string partition function
- Conformal symmetry and supersymmetry
- Coleman-Mandula theorem
- algebras
- representations
- resulting simplifications in QFT calcuations
- anomalies
- String theory basics
- specturm of open and closed strings
- string perturbation theory
- super strings and GSO projection
- D-branes from the world-volume perspective (DBI action) and from the target-space perspective (black black solution)
- AdS CFT correspondence
- near horizon limit for a stack of N D3 branes
- strong and weak for of the duality
- field-operator correspondence
- computing CFT correlation functions from supergravity solutions
- holographic renoramlization
Retake Exam: If required, the retake exam can be taken on the afternoon of Tuesday, the 18th of February 2025. The same conditions as for the exam apply.
Additional material for the individual lectures, including the exercises which we discuss in the tutorials, will appear here in due time.
- The Large N limit of SU(N) gauge symmetry and planar diagramsLecture08.11.2024 15:15, notesTutorial20.11.2024 17:15, exercise
On Wednesday the 20.11.24, we will have two tutorials and no lecture. This compensates for the shift in the course schedule due to holidays and gives you enough time to prepare for the tutorials.
Lie Algebras and Groups
Lie algebras describe infinitesimal symmetries of physical systems. Therefore, they and their representation theory are extensively used in physics, most notably in quantum mechanics and particle physics. This course introduces semi-simple Lie algebras and the associated Lie groups for physicists. We discuss the essential tools, like the root and weight system, to efficiently work with them and their representations. As on explicit application of the mathematical framework, we discuss Grand Unified Theories (GUT). Moreover, we show how modern computer algebra tools like LieART can significantly help in all explicit computations throughout the course.
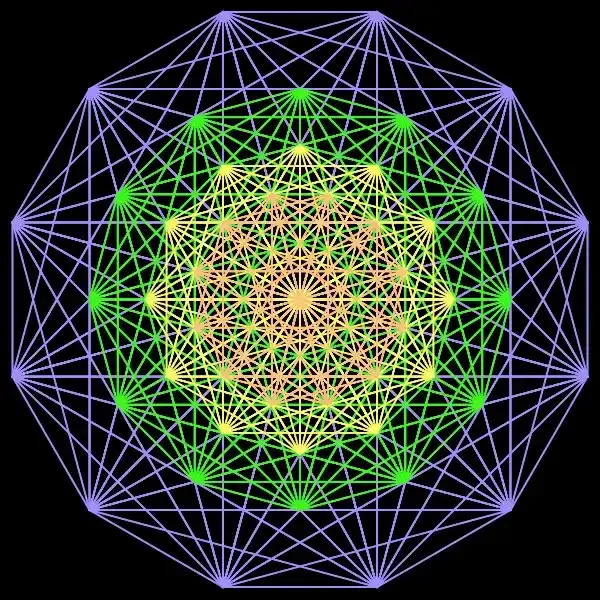 A simple example is the visualisation of the root system of projected on the Coxeter plane, which you can see here. If you want to understand how it is created and connected to particle physics, you should take this course. Basic knowledge of core concepts in linear algebra, like vector spaces, eigenvalues and eigenvectors, is assumed. Some good books about the topic are:
A simple example is the visualisation of the root system of projected on the Coxeter plane, which you can see here. If you want to understand how it is created and connected to particle physics, you should take this course. Basic knowledge of core concepts in linear algebra, like vector spaces, eigenvalues and eigenvectors, is assumed. Some good books about the topic are:
- Fuchs and Schweigert: Symmetries, Lie Algebras and Representations
- Gilmore: Lie Groups, Lie Algebras, and Some of Their Applications
- Fulton and Harris: Representation Theory
- Georgi: Lie Algebras In Particle Physics: from Isospin To Unified Theories
The article Phys. Rep. 79 (1981) 1 by Slansky and the manual of the LieART package are good references, too.
Note: At multiple occasions, we will use Mathematica and it might be a good idea to set it up on your computer. Following the instructions on the main teaching website, you should be eventually able to run the notebook, which generates the projection of the root system above.
Exam: After a majority vote, we decided together that the written exam for this course will take place on Tuesday, the 6th of February 2024, at 13:00 in room 447 (the one where we also have our classes). It will take two hours and you have a practise exam to help you preparing for it. Please be there five minutes earlier such that we can start on time.
Retake Exam: As discussed via email, you have the chance to take part in the retake exam on Thursday, the 15th of February 2024, at 13:00 in room 447. Exactly the same conditions as described for the exam above will apply. If you would like to take part in the retake exam, please send me a quick message via email such that I have an estimated head count and can bring the right number of exams.
- Introduction and motivation
- Some mathematical preliminariesLecture10.10.2023 10:15, notes
Unfortunately, there has been some problems with the WiFi in the class room and as a result the recording of the lecture is not usable. Let us hope that it will work better the next time.
- Classical matrix groupsLecture17.10.2023 10:15, notes
- Cartan subalgebraLecture24.10.2023 10:15, notes
- Root system
Sorry for the bad sound quality of the recording. I am working on this issue.
- Simple root and Cartan matrix
- Classification and Dynkin diagramsLecture14.11.2023 11:15, notes
- Irreducible representationsLecture21.11.2023 11:15, notes
Because I mentioned that you can remember the Dynkin diagram of so(8) by thinking of the flux-capacitor from Back to the Future and some of you have not see this movie here is a picutre. For me this is a classic and I highly recommend to watch it when you have not do so yet.
- Highest weight representationsLecture05.12.2023 11:15, notes
There was a small ambiguity in the Freudenthal formula for the multiplicity. The wedge for "and", looked like the V for vector space. I corrected this one in the notes. You will need this equation for the practise exam. But it is also given there.
- Characters and Weyl group
- Decomposition of tensor products and regular subalgebrasLecture19.12.2023 11:15, notes
- Special subalgebras and branching rulesLecture09.01.2024 11:15, notes
- Particle theory and the standard modelLecture16.01.2024 11:15, notes
- The Georgi–Glashow modelLecture23.01.2024 11:15, notes
Quantum Field Theory
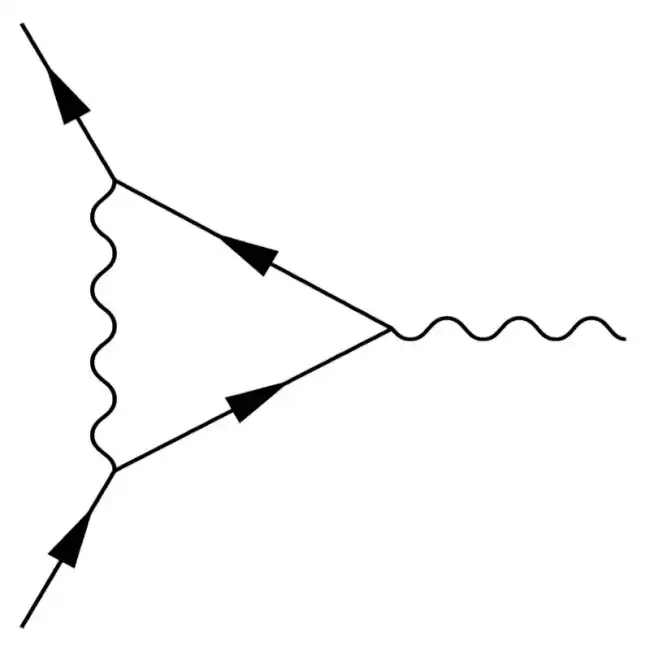 This is the mandatory Quantum Field Theory course of the Master in Theoretical Physics at the University of Wrocław. It is tailored towards master and PhD students who are familiar with
This is the mandatory Quantum Field Theory course of the Master in Theoretical Physics at the University of Wrocław. It is tailored towards master and PhD students who are familiar with
- quantum mechanics
- electrodynamics
- special relativity
- quantum electrodynamics.
There are many good books on the subject, four that I like are
- [PeskSchr] Peskin, Schroeder: An introduction to quantum field theory
- [Ryder] Ryder: Quantum Field Theory
- Weinberg: The Quantum Theory of Fields, Volume 1 & 2
- Zee: Quantum Field Theory in a Nutshell.
We will follow mostly the first one in the lectures. There will be 2 hours of lectures and 2 hours of tutorial each week. Exercises will be posted here a week before the tutorial they are discussed in. Please keep in mind that active participation in the tutorials is important to pass the course. M.Sc. Biplab Mahato will be the assistant for the tutorials. Please fell free to contact him () or me if you have any questions. For information about credits points, please refer to the syllabus or contact me directly.
Important: Students will be assigned to exercise problems by the system described here at the Thursday, 9:00 pm, before the tutorial. Please indicate your preferences by then.
Exam: After a majority vote, we decided together that the written exam for this course will take place on Monday, the 3rd of July 2023, at 14:00 in room 447 (the one where we also have our classes). It will take two hours and we will discuss a practise exam in the last tutorial to help you preparing for it. Please be there five minutes earlier such that we can start on time. Also note that you need to have more than 50% of the points from the exercises assigned to you to qualify for the exam. You can check your points here on the website, or, if you are in doubt, with me.
Retake Exam: As discussed via email, you have the chance to take part in the retake exam on Friday, the 8th of September 2023, at 17:00 in room 447. Exactly the same conditions as described for the exam above will apply. If you would like to take part in the retake exam, please send me a quick message via email such that I have an estimated head count and can bring the right number of exams.
Additional material for the individual lectures, including the exercises which we discuss in the tutorials, is given below:
- Generating functional, interactions and Feynman rulesTutorial04.04.2023 11:15, exercise
Reading: [PeskSchr] section 9.2
During the lecture and tutorial, there were several questions how to derive the symmetry factors and the Feynman rules directly from the path integral. The simple answer is of course, just expand up to the relevant order. However, this is not completely straightforward and requires a little bit care with combinatorics and Wick's theorem. Therefore, the detailed computation is attached for the propagator in theory. This hopefully helps to resolve the problem.
- Path integral for spin-1 bosons, ghost fieldsLecture18.04.2023 08:15, notesTutorial25.04.2023 11:15, exercise
Reading: [PeskSchr] section 9.4
In the second step of the Faddev-Popov procedure, we discussed during the lecture, we average over different gauge choices . We were using a Gaussian weight factor for this purpose, i.e.
At this point, the question: "Why do we use the Gaussian weight?". My answer: "Because we can compute it." is correct, but one could also use any other weight function and, after much more work, would obtain the same result. There is a nice thread on Physics stack exchange discussion this issue.
- One loop effects in QED: field-strength renormalisation and self-energyTutorial09.05.2023 11:15, exercise
Reading: [PeskSchr] section 7.1
Please take a look at the details for the derivation of the spectral density function, which we did not have time to discuss in the lecture.
- The Callan-Symanzik equation and -functionsLecture30.05.2023 08:15, notesTutorial06.06.2023 11:15, exercise
Reading: [PresSchr] sections 12.2
During the lecture, we noted that the renoramlisation condition used for massless -theory is are quite different from what we used in lecture 10 (see section 7.2 of the notes). The major challenge here is that we are dealing with a massless theory and there is a prori no mass with we can use to introduce a renormalisation scale. To overcome this problem, an imaginary mass is used to fix the renormalisation conditions which holds the physical mass (the real part of ) fixed at zero.
- Gravity, quantum gravity, one-loop -functions of a two-dimensional -model and string theoryLecture07.03.2023 09:15, notesTutorial13.06.2023 11:15, exercise
Reading: David Tong's lecture notes on String Theory section 7.1, original article Phys.Rev.Lett. 45 (1980) 1057
- Spontaneous symmetry breaking and the Higgs mechanismLecture13.06.2023 08:15, notesTutorial15.06.2023 17:00, practise exam
Reading: [PresSchr] sections 11.1 and 20.1
There is no problem sheet for this lecture. In the tutorial, which takes place right after the last lecture, we discuss the practise exam.
- BRST symmetry, physical Hilbert spaceLecture15.06.2023 15:00
Reading: [PeskSchr] section 16.2-16.4
Selected Tools of Modern Theoretical Physics 2B
 This is the mandatory Selected tools of modern theoretical physics 2B course of the Master in Theoretical Physics at the University of Wrocław. It is tailored towards master and (if interested) PhD students who are familiar with
This is the mandatory Selected tools of modern theoretical physics 2B course of the Master in Theoretical Physics at the University of Wrocław. It is tailored towards master and (if interested) PhD students who are familiar with
- linear algebra,
- analysis, and ideally
- differential geometry (from Selected Tools of Modern Theoretical Physics 2A).
There are many good books on the subject, four that I would like to point out are
- Fecko: Differential Geometry and Lie Groups for Physicists
- Naimark, Štern: Theory of Group Representations
- Barut, Rączka: Theory of Group Representation and Applications
- Zee: Group Theory in a Nutshell for Physicists
There will be 2 hours of lectures and 2 hours of labs each week. Note that we will start in the middle of the semester, after part A of this course which deals with differential geometry. Exercises will be posted here a week before the lab they are discussed in. Please keep in mind that active participation in the labs and especially submitting the solution to the posed problems is important to pass the course. M.Sc. Alex Swash will be the assistant for this course. Please fell free to contact him or me if you have any questions. For information about credits points, please refer to the syllabus or contact me directly.
Location: ATTENTION, we have two differnt rooms assigned: On Mondays will be in room 422, while on Wednesdays we will meet in room 511.
Exam: We decided together that the written exam for this course will take place on Friday, the 27th of June 2025, at 13:00 in room 320. It will take two hours (120 minutes) and we will discuss a practice exam in the last tutorial to help you preparing for it. Please be there five minutes earlier such that we can start on time. Also note that you need to have more than 50% of the points from the exercises assigned to you to qualify for the exam. You can check your points here on the website, or, if you are in doubt, with me.
Additional material for the individual lectures, including the exercises which we discuss in the labs, is given below:
- Heighest weight representationsLecture11.06.2025 10:15, notesTutorial16.06.2025 08:15, practice exam
Generalities
Mathematica
For computations we use Mathematica. It is a very powerful tool with unfortunately a quite high price for a license. Students can get a discount on licenses. If your budget is not sufficient for a student license, you can use the Wolfram Engine for Developers. After creating a Wolfram ID, it can be downloaded for free. The Wolfram Engine implements the Wolfram Language, which Mathematica is based on. But, it lacks the graphical notebook interface. Fortunately, some excellent free software called Jupyter Notebook fills the gap. Both can be connected with the help of Wolfram Language for Jupyter project on GitHub. Getting everything running might require a little bit of tinkering. But in the end, you get a very powerful computer algebra system for free. Finally, you should install LieART by following the "Manual Installation" instructions.
Assignment of problems
Solving the exercise problems for a course is very important. It helps to practice the concepts and ideas introduced during the lecture, and you will also be graded for the solutions you present during the tutorials. But at the same time, one of the most annoying questions for the students and the lecturer is: "Who would like to present his solutions to the next problem?".
Therefore, we use the following system to assign students to problems based on their preferences:
- You need to log in with your USOS account (every student at the University of Wrocław should have one). If you should be one of the few students how do not have an USOS account yet, contact me and I create an independent, temporary account for you. To log in, click on the small closed door in the top left corner of this window.
After this is done, a new window will pop up in which you should select login with USOS.
Clicking this button redirects you to the USOS login website of the university. There, you should login with your credentials, i.e. the username is the first part of your email address which comes before the @uwr.edu.pl. Note: If you do not have an USOS account, please use here the username and password you got from me.
After your first successful login, you are asked to choose a username, provide your email address and indicate your first/last name. Most important here is that you use an email address which you check regularly, because all announcements about the course will be sent to this address.
- After this is done, the small door in the top right corner which was initially closed opens up. By clicking it, you will find the following options:
Under Profile, you can edit your data, while Courses gives you a summary of the points you already have earned for solving exercise problems. Talking about problems and assignments; Every week after the lecture, a new problem sheet is published on the website. If you followed the above steps, you will get an email when it appears.
- After logging in and going to the page of your course, a new link called manage should appear behind each exercise.
By clicking it, you see a list of all problems for this exercise. It also includes the number of points you can get for each task. Problems that are marked with an asterisk (*) are optional and will not be automatically assigned. However, you can solve them to get additional points. Some problems will be presented in class for those you can choose your preferences after they are announced. You do this by dragging them into a new order (your favorite problems go to the top). After doing so, you have to save to changes by clicking the Save button. Please do not forget to click Save because otherwise your changes are not applied.
Alternatively, you can indicate that you are absent for this exercise. But note, that you can only be absent for two exercises. Hence, use this option wisely. If you choose it, no problems will be assigned to you this time. There might be also problems which are mandatory for all students in the course, like for example in Computational Methods I. In this case, you can skip this step.
- This brings us to the assignment of problems. After you indicated your preferences as described above, at a time that is fixed for every course, all problems will be assigned. The assignment happens completely automatically according to the following rules:
- At the end everybody should have approximately the same number of total, achievable points. Therefore, you can either have simpler problems with less points or a few hard ones which contribute with more points.
- If you do not indicate any preferences you get what nobody else wanted.
- If two students have the same preferences, the one who indicated them first wins.
Concluding, its in your best interest to indicate your preferences in time. After the deadline, you will receive an email with the assignment for the next tutorial. Each problem comes with two names. The first student has to present the problem in class and the second acts as a backup. The backup has to take over if the primary candidate is not able to present the solution. If the backup is doing well, s/he can get 50% of the original points of the problems as extra points. However, failure of presenting anything might also result in a 50% penalty. Therefore, if you know that for any reason you cannot present your assigned problems, please inform your backup such that they are not surprised. In addition to the assignment email, you can also find the assignments on the website.
The problems marked in red are the ones you have to present, and the ones in yellow are those for which you are the backup. By clicking on upload solution, you can upload a pdf file of your solution (this can be a photo/scan of your sheet of paper). After uploading, the problems should turn green. Don’t worry, you can still modify your solution afterwards by clicking on update solution.
After the exercise, you will also see all points which have been assigned to you here. Please make sure that you follow all instructions above and let me know if you encounter any problems.